Tense Chart In English: Rules, Examples, And Its Types
Introduction:
What Does Tense Mean?
As per the Oxford Dictionary, tense is defined as “any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb.”
Merriam-Webster Dictionary explains that the term tense refers to “a distinction of form in a verb to express distinctions of time or duration of the action or state it denotes.”
Collins Dictionary describes tense as “any of the forms of a verb which reveal the time at which an action has happened.”
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, “tense” is “any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
I. The Basics of Tenses:
Before diving into the tense chart, let’s grasp the fundamental concept of tenses. Tenses indicate when an action or state of being occurs—past, present, or future. English has three primary tenses: past, present, and future. Each tense can be further divided into four aspects: simple, continuous (or progressive), perfect, and perfect continuous.
II. The Tense Chart:
- Simple Tenses:
- Present Simple: Used for habitual actions or general truths.
- Past Simple: Describes completed actions in the past.
- Future Simple: Indicates actions that will occur in the future.
- Continuous Tenses:
- Present Continuous: Depicts ongoing actions in the present.
- Past Continuous: Describes actions that were in progress in the past.
- Future Continuous: Predicts ongoing actions in the future.
- Perfect Tenses:
- Present Perfect: Signifies actions that occurred at an unspecified time before the present.
- Past Perfect: Highlights actions completed before another past event.
- Future Perfect: Forecasts actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
- Perfect Continuous Tenses:
- Present Perfect Continuous: Indicates actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
- Past Perfect Continuous: Depicts ongoing actions that were completed before another past event.
- Future Perfect Continuous: Foretells ongoing actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
III. Rules Governing Tenses:
- Subject-Verb Agreement:
- Ensure that the verb agrees with the subject in terms of number and person.
- Time Indicators:
- Identify keywords that signal the appropriate tense, such as “yesterday” for past, “now” for present, and “tomorrow” for future.
- Irregular Verbs:
- Be aware of irregular verbs that do not follow the typical conjugation patterns.
IV. Examples:
Let’s illustrate these rules with examples:
- Simple Present: “She works in the city.”
- Present Continuous: “They are playing soccer.”
- Present Perfect: “I have visited Paris.”
- Present Perfect Continuous: “We have been studying all night.”
V. Types of Tenses:
Apart from the standard tenses, English also includes conditional tenses, subjunctive tenses, and progressive forms. Understanding these nuances adds depth to your language proficiency.
Types of Tense
In English Grammar, tenses are of three types, that is,
Verb tenses play a crucial role in expressing the timing of actions or states in a sentence. In English, there are several types of verb tenses, each serving a specific purpose. Here’s an overview of the main types of tenses:
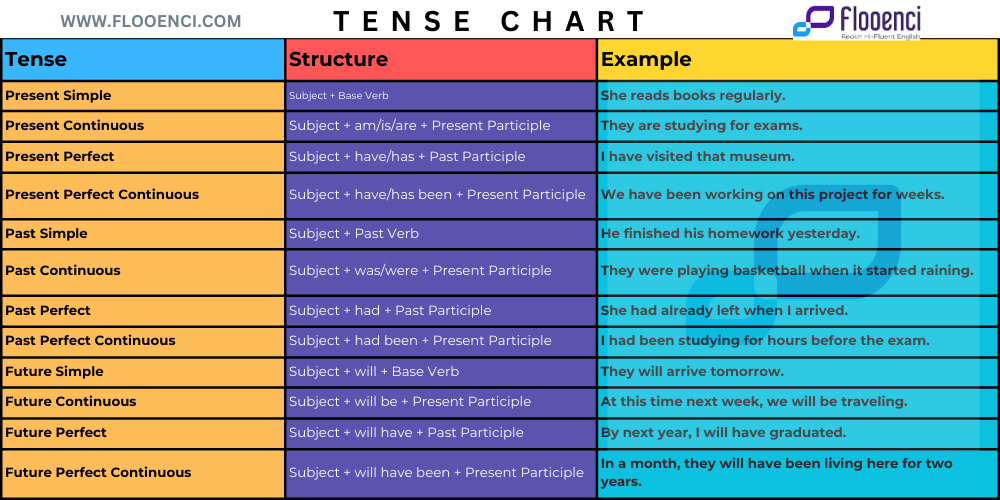
Below is a simple table representing the common English verb tenses:
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Subject + Base Verb | She reads books regularly. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + Present Participle | They are studying for exams. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + have/has + Past Participle | I have visited that museum. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + have/has been + Present Participle | We have been working on this project for weeks. |
| Past Simple | Subject + Past Verb | He finished his homework yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + Present Participle | They were playing basketball when it started raining. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + Past Participle | She had already left when I arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + Present Participle | I had been studying for hours before the exam. |
| Future Simple | Subject + will + Base Verb | They will arrive tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be + Present Participle | At this time next week, we will be traveling. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will have + Past Participle | By next year, I will have graduated. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + Present Participle | In a month, they will have been living here for two years. |
This table provides a quick reference for the structures and examples of each tense, aiding in a better understanding of their usage.
- Present Simple:
- Used for general truths, habits, and timeless actions.
- Example: “She reads books regularly.”
- Present Continuous (Present Progressive):
- Indicates actions happening at the moment or around the present time.
- Example: “They are studying for exams.”
- Present Perfect:
- Expresses actions that occurred at an unspecified time before the present.
- Example: “I have visited that museum.”
- Present Perfect Continuous:
- Highlights actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
- Example: “We have been working on this project for weeks.”
- Past Simple:
- Describes completed actions in the past.
- Example: “He finished his homework yesterday.”
- Past Continuous (Past Progressive):
- Depicts actions that were ongoing at a specific point in the past.
- Example: “They were playing basketball when it started raining.”
- Past Perfect:
- Indicates actions completed before another past event.
- Example: “She had already left when I arrived.”
- Past Perfect Continuous:
- Describes ongoing actions that were completed before another past event.
- Example: “I had been studying for hours before the exam.”
- Future Simple:
- Predicts actions that will occur in the future.
- Example: “They will arrive tomorrow.”
- Future Continuous (Future Progressive):
- Forecasts ongoing actions in the future.
- Example: “At this time next week, we will be traveling.”
- Future Perfect:
- Foretells actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
- Example: “By next year, I will have graduated.”
- Future Perfect Continuous:
- Predicts ongoing actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
- Example: “In a month, they will have been living here for two years.”
Understanding the nuances of each tense is essential for effective communication and clear expression of ideas in English.
So, in total there are 12 tenses which are as follows:
| Tenses | Tenses forms |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense |
| Present Perfect Tense | |
| Present Continuous Tense | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Past Tense | Simple Past Tense |
| Past Perfect Tense | |
| Past Continuous Tense | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense |
| Future Perfect Tense | |
| Future Continuous Tense | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
Below is the table of the examples of tenses-
| Tense | Forms | Examples |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense | He drives a car |
| Present Perfect Tense | He is driving a car | |
| Present Continuous Tense | He has driven a car | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | He has been driving a car since morning | |
| Past Tense | Simple Past Tense | He drove a car |
| Past Perfect Tense | He was driving a car | |
| Past Continuous Tense | He had driven a car | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | He had been driving the car since 7 am | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense | He will drive a car |
| Future Perfect Tense | He will be driving a car | |
| Future Continuous Tense | He will have driven a car | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | He will have been driving the car at 6 am tomorrow |
Significance of Tense Chart
The English Grammar, tenses are often considered an important concept. A verb when changing its form takes the help of tense to formulate the proper sentence or express the state of action, events, or occurrence in a proper way. It helps you to make your context clear and precise. You may also create complex sentence constructions using tenses. Therefore, you should be familiar with all twelve tenses and their usage, so that, we have made a tense chart below to help you understand better.
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples
Significance of Tense Chart
The English Grammar, tenses are often considered an important concept. A verb when changing its form takes the help of tense to formulate the proper sentence or express the state of action, events, or occurrence properly. It helps you to make your context clear and precise. You may also create complex sentence constructions using tenses. Therefore, you should be familiar with all twelve tenses and their usage, so that, we have made a tense chart below to make you understand better.
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples
| Tense Chart | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tenses | Rules and Formula | Examples |
| He had been drinking milk out of the carton when Mom walked into the kitchen. | Subject + Verb in the base form/third person plural form + the rest of the sentence | Rajesh eats bread and butter before going to school. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(am/is/are) + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | Students are going to school. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (have/has) + Past participle of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame | She has lived here all her life. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Have/Has + Been + Verb+ ing + the rest of the sentence | I have been working on this project for a week. |
| Simple Past Tense | Subject + Verb + ed / verb in the past tense + the rest of the sentence | Nupur went to the supermarket yesterday. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(was/were) + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | It was snowing today. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Past participle of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame. | She had met him before the party. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Had + Been + Verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | He had been drinking milk out the carton when Mom walked into the kitchen. |
| Simple Future Tense | Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object | I will write articles on different topics. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Subject + will be/shall be + V1 + ing + Object | I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Subject + will have/shall have + V3 + Object | I will have dressed up by the time you reach home. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object | I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock. |
Conclusion:
Mastering the tense chart in English is crucial for effective communication. By familiarizing yourself with the rules, examples, and various types of tenses, you empower yourself to express ideas with precision and clarity. Practice, coupled with a keen awareness of context, will help you navigate the intricate world of English verb tenses successfully.



